IP Telephony: A Complete Guide to Understanding IP Telephony in 2023

Preamble: Following is an article describing all that you need to know about IP telephony to exceed the voice communication demands of every tech-savvy client.
Quick Links:
1. What is an IP Telephony?
2. Benefits of IP Telephony
3. IP and VoIP Telephony
4. IP Telephony Diagram
5. How do IP Telephones work?
6. IP Telephony Deployment Models
7. Features of IP Telephony
8. IP Telephony Protocols
9. Common IP Telephony Issues
10. Frequently Asked Questions
What is an IP Telephony?
An IP (Internet Protocol) telephony is an aspect of communication that uses the internet to exchange voice messages, fax, and other types of information over the IP-based networks. In fact, it is the technology-specific term that meets the need of today’s smart communication needs.
Traditionally, this was carried over the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and based on the dedicated circuit-switched connections. However, the IP telephony simplifies it and flows the information in form of the packets across the internet or LAN (Local Area Network), bypassing the challenges of the PSTN. Simply, it is a single network infrastructure that facilitates both voice and data solutions.
Benefits of IP Telephony
1. Unified Communications (UC) Network
IP telephony is eminent for its reliable voice connectivity over LANs. With its reliability, it is also considered as the unified communications (UC) model with various valuable features, such as- supporting presence, web, video & audio conferences, and the free calls through the data network. This unified communications package will spur the growth in the organizations, without much budget to invest in it.
2. Smart Mobility/ Connectivity Solution
No doubt, IP telephony improves communication for all, even the remote workers. Today, it’s not necessary to carry the business phone with pre-paid service, wherever you travel. The IP telephony allows the remote employees to access their network using their cell phones at any location, provided the internet connection should be present there. It actually improves the connectivity at other enterprise’s stations, cities, or even countries. Hence, these mobility solutions are enhancing the employees' experience on a good note. You can read more about how this mobility solution is transforming the employee experience.
3. Easy-to-use Softphones Technology
Softphone technology is a counterpart of the teleworker solution. Actually, the softphone is a software service that you can easily download on your laptop or desktop, without the need for any hardware device. And, then, you can make a call from your laptop across the world. Once you get connected to this service, you will have access to all UC (unified communication) services. Softphone technology is embedded with a rich set of features & benefits and offering great digital calling experience. Read more about softphone technology here and see the difference.
4. Features-Rich Communication Aspect
No one can deny this fact that the IP telephony is revolutionizing the way of communication due to its rich portfolio of features. One such is that the IP phones have the potential to do much more than calling. Others may range from- teleconferencing capability, programmable buttons, auto-attendant feature, voice mail to email transcription, multi-site connectivity through the data network, unified messaging box, call waiting, and caller ID, etc. Such features set enables using IP phones more rather than the TDM systems. You can find out here more benefits of IP telephony over TDMs.
5. Easy to Install and Configure
It doesn’t require to be a pro and technical person to install and configure the IP telephones. It hasn’t the complexity of programming, proprietary software, graphical user interface, and other such confusing stuff. Simply, a person having the know-how of networks can install and configure it without any hassle.
6. Ease of Scalability
The IP telephones are not constrained by the limited number of physical phone connections. It facilitates full flexibility when there is a need for adding a new IP phone. The enterprises can easily add or remove the new or existing IP phone to/ from the router.
7. Cost Savings with Improved Productivity
For the very first time, the workers are able to communicate through one or a few primary telephone lines- inside and outside the organization. Plus, the enterprises don’t need to pay the price, levied by the telephone companies, as the analog phone lines are no longer required. Hence, the cost is decreased. Further, the IP telephony supports a great range of applications that help workers to perform their tasks faster, more efficiently, & effectively.
IP and VoIP
IP (Internet Protocol) and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol)- people often use these terms interchangeably. But there is a difference. Yet, it’s so subtle, but it does.
In a way or another- VoIP is a subset of IP. It implies- VoIP technology is based on sending only voice traffic across an IP (Internet Protocol) network- while- IP technology is based on exchanging voice, fax, and other types of data traffic.
Digitally, all elements of IP telephony utilize the digitized voice that is transmitted as the IP packets via an IP network (mostly, the LAN network). Besides, VoIP focuses on the digitization of the analog voice signals (analog to digital transformation) and are converted into binary numbers to get transferred by the IP protocol.
So, basically, in broader terms, the IP telephony is entirely a complete concept, whereas, the VoIP telephony is a mode to transmit voice to implement this concept. As for an e.g.- an IP telephony system or IP-PBX (Private Branch Exchange) containing its own VoIP and the standards (SIP, H.323), coupled with other aspects, like CRM, etc.
IP Telephony Diagram
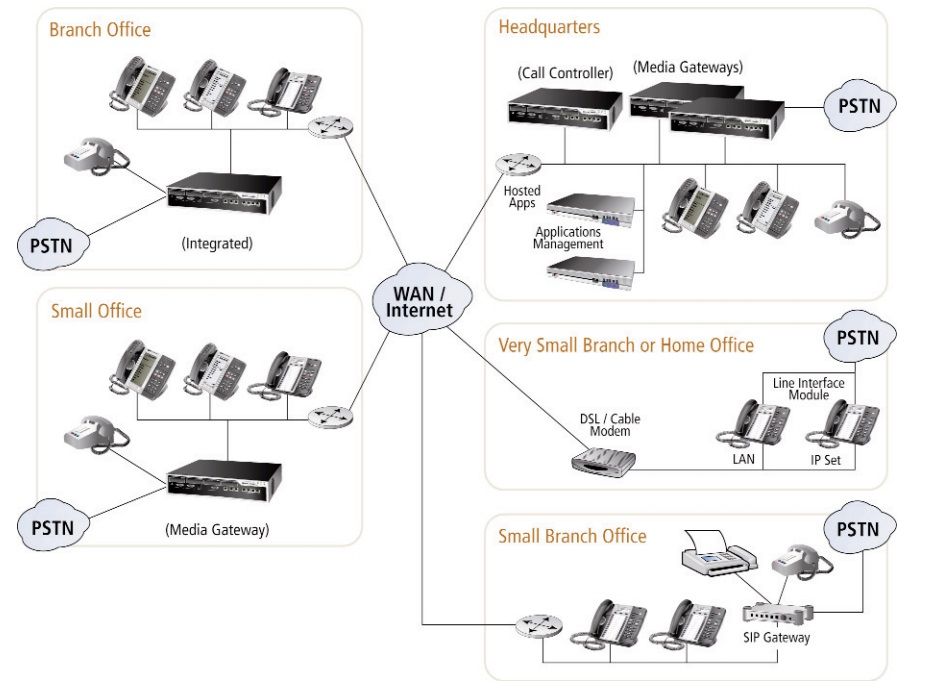
How do IP Telephones work?
Basically, the IP telephones work by scanning & detecting the individual’s analog voice signal and converting them into digital signals. Then, these digital signals are transmitted across the broadline in form of data. In simpler terms, the IP phones work by taking the phone conversations and routing them via an IP phone system across a network cable into the network, then out, and then into the internet connection.
Instead, we can say- IP phones utilize the “internet protocols” to connect and communicate through the digital mode across the internet. With this system, you can choose this technology rather than the traditional phone systems to improve communication. Simply, leverage the internet connection, the associated hardware (phone system), and the applications that make communications more effective.
Or, simply, in place of the traditional phone line and the phone network, here, the system makes use of the internet protocol and LAN to transmit the calls & other information over your office network and the phone provider’s network. And, the same protocol and network are used by computer systems, devices, and printers as well. This makes it relatively efficient you and your staff need to operate & maintain only one internal network for all communications.
Free Download: Learn how to make your business communications effective and borderless with our UCC solutions.
IP Telephony Deployment Models
You need to select the best deployment model that will go in alignment with your requirements and network. Then only, you will be good-to-go with your IP telephony working. Since, once you select the right model, it will be going to support the present as well as the future growth for voice and data. You can view different IP telephony deployment models here and pick out the one as per your stipulations.
During deployment, you may counter with many hurdles. But, your selection of the reliable model will wipe out these issues in no time. After all, the selection of today's stable model will accelerate the voice and other data delivery within your enterprise and outside it more efficiently.
Features of IP Telephony
1. HD Voice Quality
This attribute of IP telephony allows the users to leverage HD quality that leads to seamless communication, sound masking integration to wipe out the unnecessary noise, and to access- group call history, filtering & exporting, and recording management.
2. A multitude of Extensions Options
The integrated auto-routing calls feature enables the users to direct the calls automatically to one or more pre-programmed destinations. Plus, the calls will be safely & automatically routed to the next available extension. And, the voicemail box is associated with every line or extension.
3. One Number
This is one of the most flexible characteristics that allow having one & the same number to call from different handsets. Moreover, the mobile phone number is hidden make the caller won’t be able to identify your location.
There is n number of features of IP telephony in the telecommunication sector. The core point is to make the best use of the feature that will add a value-added benefit for your enterprise. You can explore more must-have features of IP telephony here and find out what you are looking for.
IP Telephony Protocols
1. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
It is a signaling protocol that is utilized to establish a “session” between the two or more participants, alter that session, and finally conclude that session. And, the real data transmission is carried by the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) on layer 5 of the OSI model.
This protocol is text-based and has much resemblance to the HTTP protocol. And, that text-based messages along with request-response mechanism make the troubleshooting easier.
2. H.323
Much like SIP protocol, H.323 is also counted in this list that has the same functionality as SIP. This protocol is also accountable for the initiation, modification, and termination of the session. It is the one from the set of standards from the ITU-T that construes an array of protocols to offer audio/visual communication across a computer network. It is actually a binary protocol that carries the voice or video over the network.
3. Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP)
Defined in RFC 1889, RTP protocol features a standard packet format for the audio/video transmission across the internet. This protocol is widely employed in communication & entertainment systems that comprise streaming media, like- telephony, television services, video teleconference applications, and web-based push-to-talk features.
As a matter of fact, RTP works hand-in-hand with RTCP (Real-time Transport Control Protocol). RTP transmits the media streams, whereas- RTCP monitors the transfer statistics, QoS, and helps in establishing the synchronization of various streams. Secondly, RTP arises from the even-number ports, and the RTCP makes use of the next higher odd-number port.
4. Real-Time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP)
This protocol is defined in RFC 3550 and works in conjunction with RTP (as discussed in RTP). This protocol is responsible for sending control packets to the participants in the specific call. In fact, the fundamental job is to provide the feedback of QoS, given by the RTP.
RTP is originated from ports of even number, while- RTCP works on the port of the next higher odd number. RTCP carries the information & statistics, like- jitter, octet & packet counts, and round-trip time. A specific application makes use of this data to control QoS parameters, and select, for e.g.- to utilize a distinct codec.
5. Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP)
SRTP is one of the security protocols utilized for the WebRTC technology and was published as RFC 3711 by IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) in 2004.
Basically, it is an extended component of RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) that adds security elements, as- message authentication, confidentiality & replay protection, mostly for VoIP communications. And, it utilizes the encryption & authentication to reduce the risks of attacks, like- denial of service.
6. Session Description Protocol (SDP)
Being published by the IETF as RFC 4566, SDP defines a specific standard to define the parameters used in exchanging media (mostly streaming media) between two endpoints. In fact, It is exclusively encapsulated within another protocol with the extensively used application, being inside of the SIP inside most of the applications.
It implies that- the SDP protocol is a declaration of its obtaining specifications and capabilities by a media endpoint. So, a distinct declaration may state:
- Which IP address is going to receive the incoming media stream.
- Which port number is attending for the incoming media stream
- What media category, the endpoint is expecting to receive (typically audio)
- Which protocol the endpoint is expecting to exchange the data in (typically RTP)
- Which compression encoding the endpoint is capable of decoding (codec)
And many more... In a typical session initiation process, the two endpoints are participating in a session. Each endpoint transmits an SDP to the other endpoint to tell about its specifications and capabilities. As a matter of fact, SDP itself doesn’t send any media but limits itself to the negotiation of a well-suited set of media exchange parameters. Even, the media streams are also handled by some different protocols and channels.
Common IP Telephony Issues
1. Need for a Power Source
IP telephony devices or handsets run on the power and take this power from the wall socket. So, there may be more chances of its failure during the local power outages, till the emergency power is available. In this case, you must have a solid power back-up to avoid such internet telephony issues.
2. Voice Compression (Codec)
If you call quality is up-to-date and you are facing the voice issue, then there must be some issue with your codec settings. This technology actually compresses the audio in order to let it flow more efficiently. In this case, you can either- follow try-and-test science with different codecs and find out which will be the best (contact your IT department for it); or- if you are confronting with sound distortion during the busiest time, then there must be some bandwidth issue. You need the bandwidth to get it checked by your IT dept. or need to upgrade the internet service.
3. Internet Service Provider’s End
If unfortunately, you are continuously facing issues frequently, then you have to reach your ISP and check their services immediately. It may be possible- the ISP may possess the periods of high latency in the connection; or- they are sending your data across the public network instead of the private one. Reach out to your provider and evaluate whether they are facing service disruptions or any network issue. In this case, it’s high time to get your problem resolved by your ISP or to switch to a new ISP.
The list doesn’t terminate here. The users can encounter multiple IP telephony errors at any time, but they can be resolved as soon as possible. Although the IP telephone systems are connected with the internet and directly or indirectly based on bandwidth, the related issues will occur. Plus, the voice and/or other data communication issues are included in the list of common issues. You can find here a few common preventable IP telephony issues and resolve them effortlessly.
Frequently Asked Questions
EPABX (Electronic Private Automatic Branch Exchange) or PABX (Private Automatic Branch Exchange) or PBX (Private Branch Exchange)- is a private telephone network, which serves the business communication in enterprises and organizations. But, IP-PBX runs digitally and is embedded with a rich set of features, including VoIP.
Therefore, as a matter of fact, IP-PBX and EAPBX basically have the same functionality. However, EPABX is utilizing analog technology at a certain level. So, the companies prefer the IP-PBX over EPABX, most primarily to avoid the complexity of wires. If you want to know the benefits of using IP-PBX, then you can read here- IP-PBX vs EPABX.
Technically, IP Telephony is something associated with packet-switching, while PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) is related to circuit-switching.
In simple language, with PSTN, there is a direct connection between two communicating voice parties via a dedicated circuit. And, that circuit is completely reserved for a single contact. And, with IP telephony, multiple packets are passing through a single communication line. And, the voice packet of one or more conversations may or may not travel via that same path, as other packets are transmitting data, video, etc.
With this, we can determine that the PSTN is something traditional that needs a huge number of assets, and IP telephony is a modern system that makes everything simpler just by the internet.
Yes, it does. But it requires a specialized voice gateway that converts the IP packets from the IP telephone systems into the TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) voice to be sent over the traditional PSTN network. Thus, the action occurs.
SIP (Session Initiated Protocol) and PRI (Primary Rate Interface) are two different technologies that connect your business to PSTN. Still, the “way” differs. SIP trunks are utilized to send voice and data via the internet (virtually), whereas- PIR trunks are employed to send voice and data through the physical dedicated line.
Apart from that- SIP needs little or no hardware investment for deployment, while- PRI needs the complicated setup, maintenance, and up-front investment in hardware. Still, finding difficulty to take the decision? PRI vs SIP Trunking is here to help you out.
Wherever there is an internet connection, you can use your IP phones. They don’t rely on any brick-and-mortar location. You can easily unplug your IP phone, carry it to some other place, and plug it again while your line (phone number or extension) and its associated settings remain unaltered.
Yes, there are specific telephone handsets that are exclusively engineered to carry the IP communication across the network hassle-free. Such telephone systems are available at most international manufacturers of telephony products, such as- Mitel, Panasonic, Counterpath, Aastra, Cisco, GrandStream, etc.
“Voice” is the main ingredient of telephony communication and thus, a minor issue has a great impact on the entire conversation. So, you have to make sure that there will be no delay, no jitter, no bandwidth issue, no compression problem, etc. To resolve such issues, you can use state-of-the-art technology that must be in sync with communication lines, routers, bandwidth usage, etc.- to avoid any type of chaos while on call.
Since voice disruption leads to degraded performance and no one wants it. To wipe out this issue, the high-capacity lines, along with powerful routing equipment (e.g. routers and large enough switches) come into use. Thus, they cost a lot. To resolve it, set the prioritization of voice packets with respect to other data. The price will drop, and you will receive the optimum experience at the other end.
The usage of IP telephony technology is considered as a medium to long-term business. And, according to the studies, the packet-switched networks that are used for voice communication is more economical than the circuit-switched networks. The rationale being is that the circuit-switched network makes use of the entire communication line for just one conversation as compared to the packet-switched network. Hence, the cost will automatically rise.
Further, when the communication line travels among different locations or cities or states or countries, then using a private network is secure and far more cost-effective than employing the public network.
In the nutshell, IP telephony is a much more reasonable and viable option than the legacy telephone solutions.